Back and Joint Pain
What Is A TFCC Tear Of The Wrist?
Anatomy And Function Of The TFCC
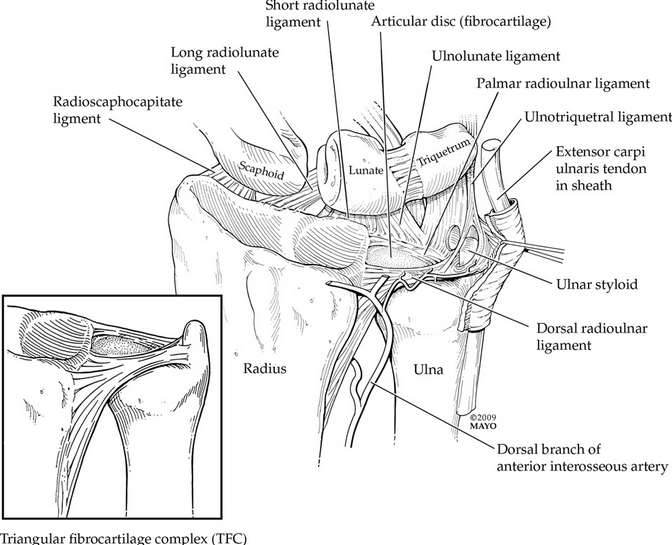
The triangular fibrocartilage complex, or TFCC for short, is as the name would suggest a complex of structures. The TFCC is located on the little finger side of the wrist and is comprised of ligaments, cartilaginous structures and a tendon sheath. The triangular fibrocartilage complex separates the radiocarpal from the distal radioulnar joint. Occupying the area between the radius and ulna at the wrist (the two main long bones, that make up the forearm). The function of the triangular fibrocartilage complex is that of stabilization of the wrist. It helps your wrist move by stabilising the forearm bones (distal radioulnar joint stability), when grasping objects or rotating your arm. It also helps cushion and support the small bones of the wrist on the little finger side, providing ulnocarpal stability.
Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Tears
A triangular fibrocartilage complex tear can cause chronic wrist pain in some people and there are typically two types of TFCC tears (Type 1 and Type 2).
- Traumatic Tears: A traumatic tear is frequently the result of a fall and are these are referred to as the Type 1 TFCC tears.
- Degenerative Tears: These are chronic tears, tears that occur over a period of time, typically the prevalence of these type of tears increase with age and are referred to as Type 2 TFCC tears.
Symptoms Of TFCC Tears
The main symptom of a triangular fibrocartilage complex tear is pain felt along the little finger side of the wrist, however sometimes pain may be experienced throughout the entire wrist. Any pain experienced with a triangular fibrocartilage complex tear will generally be made worse with moving the wrist from side to side. It may also be aggravated by doing simple functional tasks like turning a key in a lock. Likewise, when pressure is applied to the wrist, such as pushing your self up to when rising from a chair, or doing a press up of bench press type exercise commonly causes pain with triangular fibrocartilage complex complaints.
Other triangular fibrocartilage complex tear symptoms may include:
- A clicking or popping sound frequently associated with pain when moving the wrist into certain positions.
- Tenderness on palpation and swelling in the wrist, specifically on the little finger side of the wrist.
- Weakness of the wrist, this may be noted as a reduction in grip strength with functional activities around the home or workplace, or with lifting activities at the gym.
Disclaimer: Sydney Physio Clinic does not endorse any treatments, procedures, products mentioned. This information is provided as an educational service and is not intended to serve as medical advice. Anyone seeking specific orthopaedic advice or assistance on What Is A TFCC Tear Of The Wrist? should consult his or her general practitioner, sports medicine specialist, orthopaedic surgeon or physiotherapist.