Back and Joint Pain
What Is Gout And Who Gets It?
What Is Gout?
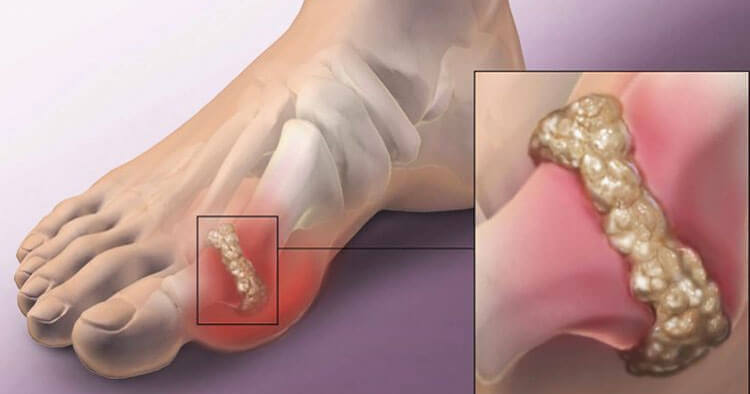
Gout is a common form of inflammatory arthritis causing painful inflammation of the affected joints. It is characterized by recurrent attacks of swelling, redness and extreme pain in the affected joint/s. Unlike most other types of arthritis that develop slowly, gout comes on suddenly (often overnight). The most commonly affected area is the big toe joint although the ankles, knees, elbows, wrists and hands (and any other joint can be affected).
Gout is caused by a build up of a waste material called uric acid in the bloodstream. Uric acid comes from the breakdown of food, drinks, cells and DNA and is excreted from the body by the kidneys. When there is too much uric acid in the bloodstream it is called hyperuricaemia. With gout excess uric acid that is not excreted by the body settles in joints in the form of tiny crystals (called ‘urate’). This causes sudden inflammation, swelling and pain.
What Are The Potential Causes?
Someone is more likely to have an attack when they have elevated levels of uric acid in the blood. The build up of uric acid in the body (hyperuricaemia) is most commonly caused by the under excretion of uric acid by the kidneys. However hyperuricaemia may also be caused by the overproduction of uric acid. This can be hereditary yet other causes such as the use of fluid tablets (diuretics) can cause the retention of excess uric acid. Not everybody with hyperuricaemia develops gout hence other factors must be important.
Other Listed Risk Factors Include:
- Consuming too much alcohol (particularly beer and port)
- Diet high in ‘purines’ such red meat, oily seafood or sugary drinks.
- Being Overweight
- Type 2 Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Kidney disease
- Crash dieting or fasting
- Dehydration
- Surgical operation or injury to a joint
- Being unwell or suffering with fever
Who Gets Gout?
Gout is more common in men (reported as much as 10 times more common in men than females). The hereditary component is reinforced as it is not uncommon for several men of the one family to be affected. Gout is rare prior to puberty, being more common in older people than the young, it is uncommon in women to suffer with the condition before menopause. High risk include Maori and Pacific Islander’s as they tend to have high uric acid levels (hyperuricaemia) predisposing them, however it can affect anyone.
Disclaimer: Sydney Physio Clinic provides this information as an educational service and is not intended to serve as medical advice. Anyone seeking specific advice or assistance on What Is Gout And Who Gets It? should consult his or her physiotherapist, general practitioner or otherwise appropriately skilled practitioner.