Back and Joint Pain, Sports Injuries and Management
Diagnostic Imaging And Physiotherapy
Diagnostic Imaging By Computed Tomography
Previously referred to as a CAT scan, diagnostic imaging by computed tomography also commonly known as a CT scan combines multiple X-ray images into a 3D model.
An analogy for CT scanning is like taking slices through a loaf of bread, where a CT scan is a way of using X-rays to take images in very fine slices through a part of the body.
How Computed Tomography Works
At the completion of the scan the thin picture slices can be put together reconstructing the body part (as you may reconstruct the loaf of bread once sliced). Once the images are put back together then the radiographer can cut it into the slices that will help the person viewing the scan see the parts of the body that are of interest. Each scan is specifically created for the area of the body and condition that is under investigation.
Through the different slices and 3D reconstructions you get a very detailed picture of the area of the body being examined.
- CT scans can clearly show very small bones as well as the surrounding tissues such as muscle and blood vessels. CT scanning is invaluable in diagnosing and treating spinal problems as well as injuries to the hands, feet, ankles and other skeletal structures.
Risks Verses Benefits Of Diagnostic Imaging By Computed Tomography
CT scans are a fast, effective and accurate diagnostic imaging technique. They are generally safe however some people may be allergic to the iodinated contrast given (if a contrast dye is used in the imaging process). Individuals allergic to the iodinated contrast may experience some of the following symptoms:
- Skin rash or hives.
- Nausea and/or vomiting.
- Dizziness and/or headache.
- Itching.
- Sneezing and/or watering eyes.
- Gagging or feeling of suffocation or swelling of the inside of the throat or mouth.
- Change in blood pressure.
As with X-rays radiation exposure is the major risk of having a CT scan. A CT scanner uses X-rays to obtain the pictures and because of the number of slices / pictures taken with a CT scan the amount of radiation with this form of diagnostic imaging is greater than what an individual is exposed to with plain X-rays.
Getting Referred For A CT Scan By Your Physiotherapist
A Sydney physio can refer you for computed tomography imaging however physiotherapists can not be bulk billed through Medicare for CT scans to any part of the body.
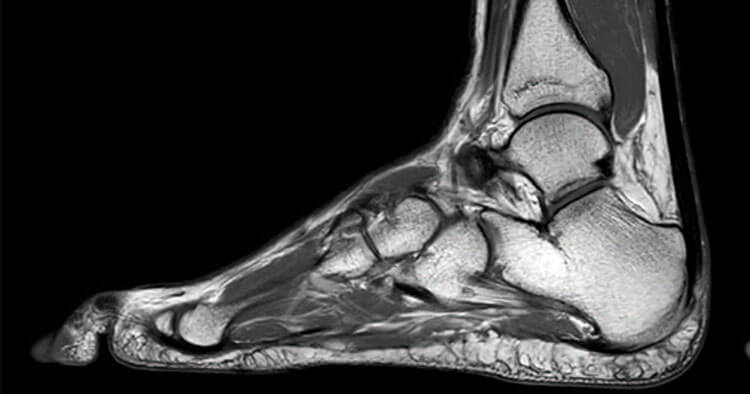
Diagnostic Imaging By MRI
An MRI or magnetic resonance imaging is a diagnostic imaging procedure that uses strong magnets and radio-frequency pulses to generate signals from the body. The signals are detected by a radio detector and processed by a computer to create pictures of the inside of the body.
An MRI is capable of providing a wide range of information about your body via high-quality images. An MRI when used in physiotherapy is very useful in imaging complaints like joint sprains, muscle or tendon strains and structures responsible for spinal pain. Magnetic resonance imaging is particularly useful in when used in physiotherapy in assessing:
- Ligament injruies including ACL ruptures of the knee or ankle sprains.
- Lumbar or cervical disc injury.
- Tendinopathy such as with the Achilles tendon, hamstring or rotator cuff.
- Meniscal or labral injuries to the knee, hip or shoulder as well as joint surface injury such as bone bruising and osteochondral damage.
Risks Verses Benefits Of Diagnostic Imaging By MRI
MRI unlike X-ray or CT imaging does not use radiation. An MRI therefore is considered safe for children and can also be used safely in pregnancy. There are no reported effects of an MRI on an unborn child, but as always caution is used in pregnancy.
Because the MRI uses a very strong magnet, a risk of having an MRI is if the individual has any implants or objects that can not go in the scanner due to interactions of the objects with magnetic fields. There is the possibility that metal objects previously implanted in the body may move, get hot or experience electrical currents leading to malfunction of the device.
AS with CT imaging and the use of a contrast dye, there is a very small risk of an allergic reaction to the contrast dye used with some individuals if having a contrast MRI.
Getting Referred For An MRI Scan By Your Physiotherapist
A Sydney physio can refer you for magnetic resonance imaging however physiotherapists can not be bulk billed through Medicare for MRI scans to any part of the body.
Disclaimer: Sydney Physio Clinic provides this information as an educational service and is not intended to serve as medical advice. Anyone seeking specific advice or assistance on Diagnostic Imaging And Physiotherapy should consult his or her general practitioner, physiotherapist, sports medicine specialist, orthopedic surgeon or otherwise appropriately skilled practitioner.