Back and Joint Pain, Sports Injuries and Management
Treatment For Osteitis Pubis
Diagnosing Osteitis Pubis
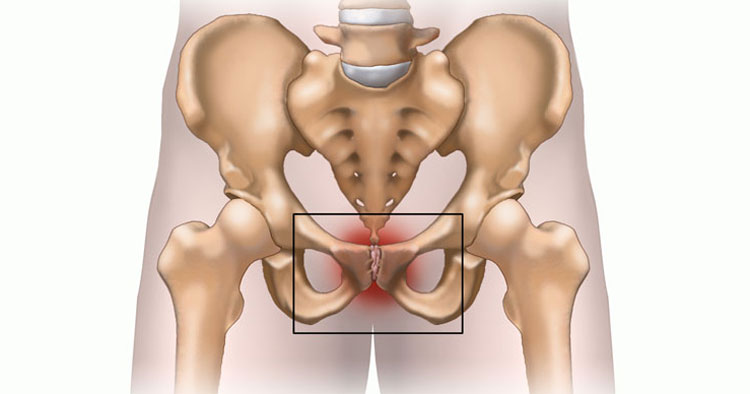
Treatment for osteitis pubis ideally starts with early diagnosis to help prevent the condition progressing beyond the stage of bone stress. However osteitis pubis diagnosis is often made in the more advanced stages of the condition, when there are signs of erosion of the pubic bones at the pubic symphysis. Clinical suspicion for a diagnosis of osteitis pubis is often the result of the subjective history of the complaint and some assessment signs as highlighted below:
- Pain with osteitis pubis is typically experienced over the pubic symphysis and may have accompanying referred pain into the groin region, with the pubic symphysis and pubic ramus being tender on palpation.
- Resisted muscle testing of the hip flexors and adductors will frequently elicit pain, as will stretching these muscle groups through the appropriate hip movements.
- Coughing/sneezing and performing a sit up will also frequently reproduce pain.
There are many potential causes of groin region pain, other conditions that may give a similar presentation may include pain coming from a tendon strain, hernia, or the hip joint… accurate diagnosis as in all circumstances allows for appropriate treatment planning.
Investigations Used In Diagnosing Groin Pain
Investigations often used that can assist in diagnosis and help appropriately plan treatment for osteitis pubis include:
- The use of X-rays may in advanced cases highlight erosion of the pubic symphysis. X-rays can also appear normal, especially early on in the presentation of the condition.
- MRI can pick up signs of bone stress and swelling in the area.
- A Bone scan if positive for osteitis pubis will highlight advanced uptake at the pubis symphysis and is very sensitive for picking up change.
Treatment For Osteitis Pubis
Frustratingly one of the keys to treating osteitis pubis is rest. It is typically the result of overloading through running, jumping, kicking and refraining from these and other aggravating activities to allow things to settle is necessary. Beyond just rest, treatment focuses on symptomatic relief from therapeutic aids such as ice and the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) being commonly used. Physiotherapy incorporating exercise prescription targeted at bringing stability to the pelvis is important when looking towards a return to the aggravating activities and avoid relapses in symptoms. The prescription of a sacral belt may also be offered, some individuals find such supports useful as sacral belts work to increase stability around the joints of the pelvis assisting weaker muscles, helping provide the necessary stability to reduce pain and allow increased activity. Even with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment it is not uncommon for the rehabilitation process with osteitis pubis to take a few months to successfully return to sport making it a highly frustrating injury for athletes to suffer.
Disclaimer: Sydney Physio Clinic does not endorse any treatments, procedures, products mentioned. This information is provided as an educational service and is not intended to serve as medical advice. Anyone seeking specific advice or assistance regarding Treatment For Osteitis Pubis should consult his or her general practitioner, sports medicine specialist, or physiotherapist.