Muscle Pain and Tendinopathy, Sports Injuries and Management
Trochanteric Bursitis The Most Common Type Of Hip Bursitis
What Is A Bursa?
A bursa is a closed fluid-filled sac, bursae function as a gliding surface in the body, there to help reduce friction between moving tissues, acting as cushions between bones and soft tissues such muscles, tendons, and skin. All the major bursae of the body are located near the large joints of the body like the knees, elbows, hips and shoulders… These bursae sit adjacent to the tendons around these large joints and when a bursa becomes inflamed, the resulting condition is known as “bursitis”whereby an individual with an inflamed bursa at the hip would be referred to as having hip bursitis.
The Types Of Hip Bursitis
The most common type of hip bursitis involves the greater trochanteric bursa, typically referred to as trochanteric bursitis, or greater trochanteric pain syndrome (GTPS). This form of bursitis will commonly cause pain around the lateral hip area.
Ischial bursitis, another common bursitis of the hip causing pain in the upper buttock area and Iliopsoas bursitis, a bursae that causes pain in the front of the hip area. However the purpose of this blog is to briefly outline greater trochanteric pain syndrome so when referencing “hip bursitis” assume what is being referred to is trochanteric bursitis.
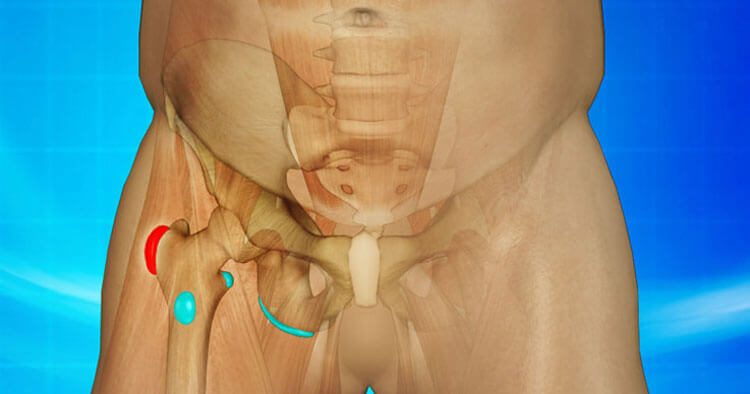
What Is Trochanteric Bursitis?
Trochanteric bursitis is one of the most commonly diagnosed bursitis in the body and the most common in the hip, frequently causes discomfort and local tenderness in the outer hip area. Anatomically the superficial trochanteric bursa lies over the prominent bone on the side of your hip known as the greater trochanter and may become irritated if the hip is overused or injured.
- Pain associated with trochanteric bursitis often causes dull pain locally on the outer hip, a pain which may radiate to the thigh and as far as the knee.
- The pain may make it uncomfortable for individuals to lie on the affected side, often causing significant sleep disturbance.
- Functionally the pain associated with trochanteric bursitis may be brought on by rising from a deep chair following a period of prolonged sitting, or sitting with legs crossed.
- The pain with trochanteric bursitis may also be aggravated with walking, negotiating stairs and exercise. Adults who are regularly active and run, walk, cycle may be susceptible to developing greater trochanteric pain syndrome, potentially due in some part to the iliotibial band (ITB). The ITB is a long band of connective tissue running from the hip to the knee this band can “rub” against the trochanteric bursa potentially causing irritation when performing these repetitive activities. Therefore a “tight” ITB as a potential source of friction against the trochanteric bursa is considered to be a possible cause of bursitis.
Other causes, risk factors, diagnosis and treatment approaches will be discussed in later blogs.
Disclaimer: Sydney Physio Clinic provides this information as an educational service and is not intended to serve as medical advice. Anyone seeking specific advice or assistance on Trochanteric Bursitis One Of The Most Common Types Of Bursitis should consult his or her physiotherapist, general practitioner or sports medicine specialist.